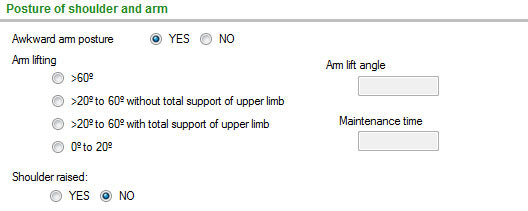Developed by the International Standardisation Organisation in 2000.
It assesses static working postures. It has the capacity to evaluate all the postures adopted during the performance of a task in a global manner. It is this capacity to evaluate multiple tasks that makes it one of the most commonly used to assess postural load.
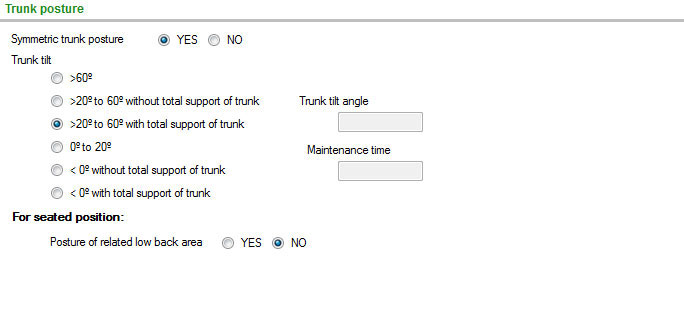
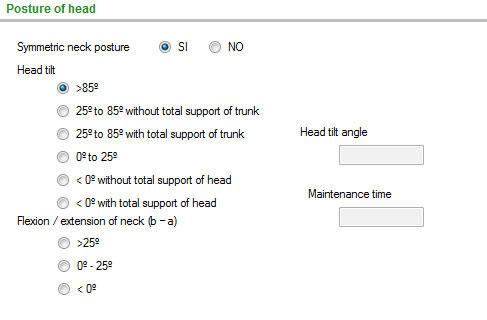
It analyses several segments and joints separately, in two steps. In the first step, the joint angles are considered, recommending some values based mainly on the strain risk of the passive body structures (ligaments, cartilages, intervertebral discs). In the second step, the maintenance of the posture is taken into account.